

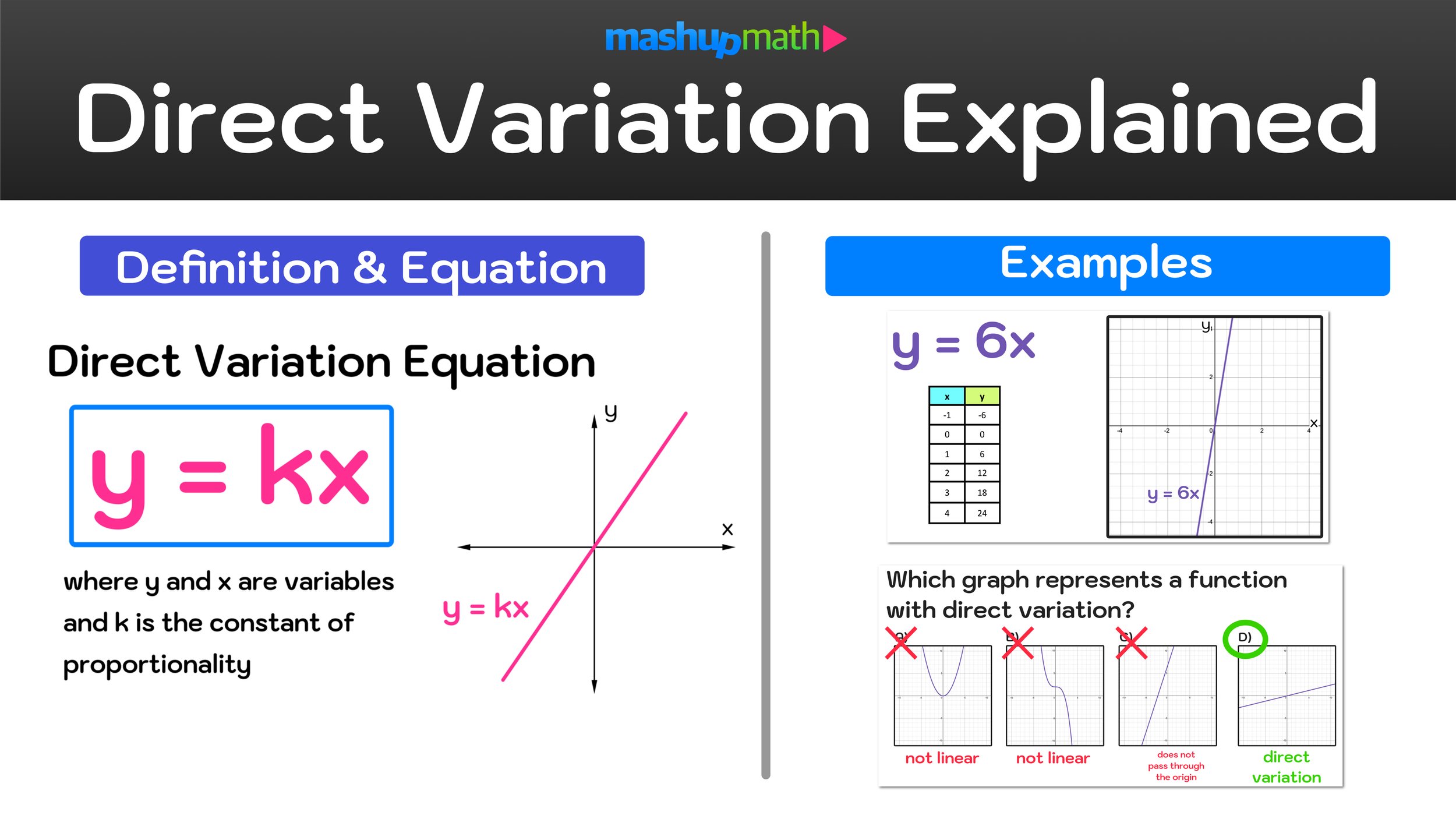
Whenever you are learning about linear functions and linear relationships in algebra, you will eventually come across a concept called Direct Variation, which refers to a proportional linear relationship between two variables, x and y. This short guide will teach you everything you need to know about direct variation and covers the following topics:
Now, let’s start off by learning some key definitions and characteristics about the concept of direct variation.
What is a direct variation? In math, direct variation is a proportional linear relationship between two variables that can be expressed as the equation y = kx, where y and x are variables and k is a constant.
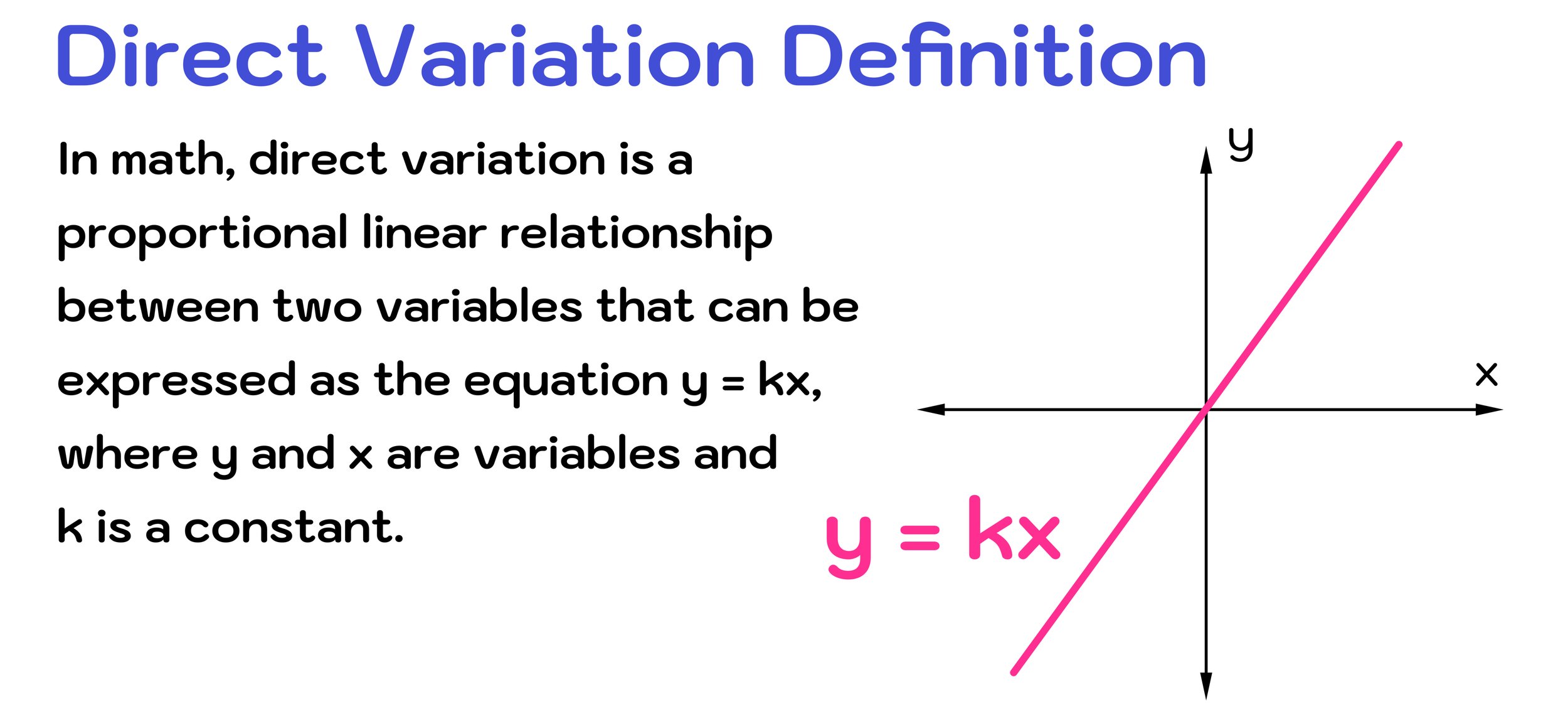
According to the direct variation definition, direct variation means that as x increases, y also increases proportionally. Similarly, as x decreases, y also decreases proportionally. In other words, if two quantities are related to each other in such a way that when one quantity increases, the other quantity increases by a proportionally, then you can say that the quantities vary directly with each other.
What are direct variations in real life? An example would be a train that is moving at a constant speed, the distance it covers over a given time period is directly proportional to its speed. If the train doubles its speed, it will cover the twice the distance in that same amount of time. In this example, the direct variation formula would be y = kx where y equals distance travelled, k equals the speed, and x equals time.